How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and responsible drone operation. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, capturing stunning aerial footage and respecting all relevant regulations.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone navigation, camera operation, and troubleshooting, equipping you with the knowledge to handle various situations. Understanding the legal and safety aspects is paramount, and we’ll delve into those crucial details as well, ensuring you fly responsibly and legally. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide will serve as your comprehensive resource.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before you even think about taking off, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting key components, verifying legal compliance, and understanding potential risks. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage, and legal repercussions.
Pre-flight Inspection Steps
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures your drone is in optimal condition for flight. Follow these steps systematically:
- Battery Check: Verify the battery level is sufficient for your planned flight time, considering factors like wind and payload. Inspect the battery for any physical damage, swelling, or leaks.
- Propeller Check: Carefully examine each propeller for cracks, chips, or bends. Ensure they are securely fastened to the motors.
- GPS Signal Strength: Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. A weak signal can lead to inaccurate positioning and control issues.
- Gimbal and Camera Check: Inspect the gimbal for smooth movement and ensure the camera lens is clean and free from obstructions.
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a visual inspection of the entire drone, checking for any loose parts, damage, or unusual wear.
- Controller Check: Ensure your controller is fully charged and properly connected to the drone. Check the responsiveness of the sticks and buttons.
- Software Update: Check for and install any available firmware updates for both the drone and the controller. These updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements.
Pre-flight Checklist Table
This table provides a structured format for your pre-flight checks. Remember to adapt it to your specific drone model.
| Manufacturer | Model | Component | Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI | Mavic 3 | Battery Level | [ ] Sufficient charge; no damage |
| DJI | Mavic 3 | Propellers | [ ] Securely fastened; no damage |
| Autel | Evo II | GPS Signal | [ ] Strong signal acquired |
| Parrot | Anafi | Gimbal | [ ] Smooth movement; no obstructions |
| Any Manufacturer | Any Model | Overall Drone Condition | [ ] No loose parts; no visible damage |
| Any Manufacturer | Any Model | Controller Connection | [ ] Properly connected; fully charged |
| Any Manufacturer | Any Model | Firmware | [ ] Up-to-date |
Legal and Safety Regulations
Drone regulations vary significantly by location. Before flying, research and understand the specific laws and airspace restrictions in your area. This includes registration requirements, flight restrictions near airports and sensitive areas, and limitations on flight altitude and distance.
Familiarize yourself with the rules regarding privacy and data protection. Always respect the privacy of individuals and avoid filming people without their consent. Be aware of potential liabilities for accidents or property damage.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering the art of drone operation takes practice and patience, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Mastering your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Understanding the different control schemes and how to calibrate your drone’s systems will enhance your flying experience.
Basic Drone Controls

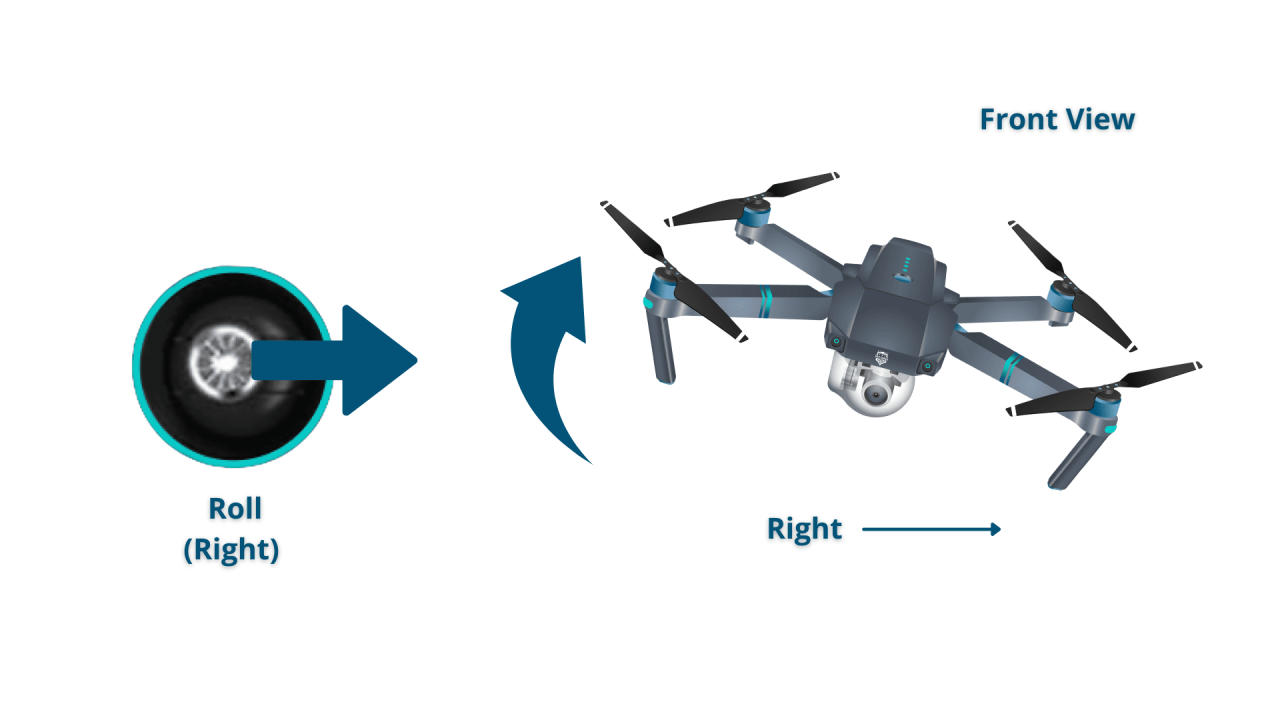
Most drones use a pair of joysticks for primary control. One stick typically manages throttle (up/down) and yaw (rotation), while the other controls roll (tilt left/right) and pitch (tilt forward/backward). Buttons and switches on the controller provide access to additional features like camera control, flight modes, and return-to-home.
Control Schemes
Different drones may use slightly different control schemes. Some offer customizable settings to adjust the responsiveness of the controls. Understanding the differences and adjusting the settings to your preferences is essential for comfortable and precise control. For example, Mode 2 and Mode 1 are common configurations with different stick assignments.
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating your drone’s compass and GPS is vital for accurate navigation and stable flight. A miscalibrated compass can cause erratic behavior, while GPS issues can lead to inaccurate positioning and loss of control. Most drones provide on-screen instructions for performing these calibrations.
- Compass Calibration: Follow the drone’s instructions to perform a compass calibration. This typically involves rotating the drone slowly in a figure-eight pattern.
- GPS Calibration: Allow the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This usually takes several minutes and requires a clear view of the sky.
Takeoff, Hover, and Landing, How to operate a drone
Smooth and controlled takeoff, hovering, and landing are crucial for safe drone operation. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
- Takeoff: Gently increase the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Maintain a steady throttle to avoid jerky movements.
- Hover: Practice maintaining a stable hover position. Use small, precise adjustments to the sticks to counteract any drift caused by wind.
- Landing: Gradually lower the throttle until the drone gently touches down. Avoid abrupt landings, which can damage the drone or its components.
Flight Modes and Camera Operation
Understanding your drone’s flight modes and camera settings is key to achieving optimal image quality and safe flight. Different modes cater to varying skill levels and flight situations, while camera settings allow for creative control over your footage.
Flight Modes
Most drones offer various flight modes, each designed for specific purposes and skill levels. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers. Manual mode offers complete control but requires significant skill and practice.
| Flight Mode | Description | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Limited speed and responsiveness | Beginner |
| Sport | Higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers | Intermediate |
| Manual | Complete control over all aspects of flight | Advanced |
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows you to control the exposure and image quality. Understanding the interplay between these settings is crucial for capturing professional-looking photos and videos.
Camera Features Comparison
Different drones offer varying camera features, impacting image and video quality. Consider factors like sensor size, resolution, frame rate, and dynamic range when choosing a drone.
| Feature | Impact on Image/Video |
|---|---|
| Sensor Size | Larger sensors generally produce better image quality with less noise |
| Resolution | Higher resolution means more detail, but also larger file sizes |
| Frame Rate | Higher frame rates allow for smoother slow-motion footage |
| Dynamic Range | Wider dynamic range captures more detail in both highlights and shadows |
Recording and Saving Footage
Most drones offer simple recording and saving options. Ensure you have sufficient storage space on your drone’s SD card before starting a flight. After landing, safely remove the SD card and transfer your footage to a computer for editing and post-processing.
Advanced Maneuvering and Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, exploring advanced maneuvers and techniques can significantly enhance your aerial photography and videography. This section will explore techniques for smooth and precise movements, utilizing waypoints and automated flight plans, and capturing cinematic shots.
Smooth and Precise Drone Movements
Achieving smooth and precise drone movements requires practice and understanding of your drone’s responsiveness. Techniques like panning, tilting, and orbiting allow for creative camera angles and dynamic shots. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting them in more complex environments.
Waypoints and Automated Flight Plans

Many drones allow you to program waypoints, creating automated flight plans. This feature is invaluable for capturing complex shots or covering a large area. Plan your flight path carefully, considering obstacles and potential hazards.
Cinematic Shots
Cinematic shots, such as tracking shots and aerial perspectives, add a professional touch to your footage. These shots require precise control and planning. Practice these maneuvers in a safe environment to perfect your technique.
Flight Plan Example
For filming a building, a possible flight plan would involve establishing shots from various distances and angles, followed by close-up shots of architectural details. Consider using waypoints to create smooth transitions between shots.
For landscape footage, a flight plan might involve a sweeping panoramic shot, followed by close-ups of interesting features, such as waterfalls or mountain peaks. Using automated flight plans can streamline the process and ensure consistent shot quality.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even experienced drone pilots encounter occasional problems. Understanding common issues and their solutions can save you time and frustration. This section provides guidance on resolving common problems and performing basic maintenance.
Common Drone Problems
Several common issues can arise during drone operation. These include low battery, GPS signal loss, propeller malfunction, and communication problems. Knowing how to identify and address these issues is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
Troubleshooting Steps
Addressing these problems often involves a systematic approach. Check the obvious first (battery level, GPS signal, propellers), then consider more complex issues like software glitches or hardware malfunctions. Consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting instructions.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe operating procedures, which you can find detailed information on at how to operate a drone. Ultimately, responsible operation ensures both the safety of your drone and those around you, making for a successful and enjoyable flight experience.
Common Problems, Causes, and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge; high power consumption | Charge battery; reduce flight time; reduce payload |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions; weak signal | Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky; wait for a stronger signal |
| Propeller Malfunction | Damage; loose fastening | Replace damaged propellers; tighten loose fasteners |
| Communication Issues | Distance; interference | Reduce distance; move to an area with less interference |
Basic Drone Maintenance
Regular cleaning and battery care extend your drone’s lifespan and maintain its performance. Clean the drone after each flight, removing dirt and debris. Store batteries properly to prevent damage and extend their lifespan.
Drone Photography and Videography Tips
Capturing high-quality photos and videos with a drone requires understanding composition, framing, lighting, and weather conditions. This section will provide tips for improving your aerial photography and videography.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Use the highest resolution and frame rate settings your drone allows, ensuring sufficient storage space on your SD card. Experiment with different camera settings to achieve the desired look and feel for your shots. Proper lighting and stable conditions will significantly improve image quality.
Principles of Composition and Framing
Apply the rule of thirds and lead lines to create visually appealing compositions. Use framing techniques to highlight your subject and create depth in your shots. Consider the background and its impact on the overall composition.
Shot Types and Their Uses
Different shot types serve different purposes. Establishing shots provide context, while close-ups highlight details. Aerial perspectives offer unique viewpoints. Choose the appropriate shot type to tell your story effectively.
Lighting and Weather Conditions
Lighting significantly impacts image quality. The “golden hour” (sunrise and sunset) offers soft, warm light, ideal for photography and videography. Avoid harsh midday sun, which can create strong shadows and overexposure. Adverse weather conditions can affect flight safety and image quality; always prioritize safety.
Drone Regulations and Responsibilities: How To Operate A Drone
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety and privacy. Understanding these aspects is crucial for avoiding legal issues and ensuring safe operations.
Importance of Following Local Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary widely depending on location. It is the pilot’s responsibility to research and comply with all applicable laws and regulations before flying. Failure to comply can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges.
Responsibilities of a Drone Pilot
Drone pilots have a responsibility to operate their drones safely and responsibly. This includes respecting the privacy of others, avoiding crowded areas, and being aware of potential hazards. Always maintain visual contact with your drone, and be prepared to land immediately if necessary.
Safety Considerations When Flying Near People or Property
When flying near people or property, maintain a safe distance and avoid causing any disturbance or damage. Be mindful of potential hazards, such as power lines, trees, and buildings. Always prioritize safety over capturing a specific shot.
Airspace Restrictions and Regulations
Airspace restrictions and regulations vary depending on location and the type of airspace. Always check for any restrictions before flying, and avoid flying near airports or other restricted areas. Use online resources or apps to check airspace restrictions in your area.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding experience, opening up a world of creative possibilities. From breathtaking aerial photography to efficient data collection, the applications are vast. Remember, responsible piloting is key – always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continuously learn and improve your skills. With practice and a solid understanding of the fundamentals, you’ll be capturing stunning visuals and exploring the skies with confidence.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s recommended to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or experiencing erratic flight behavior.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode and carefully bring the drone down. Most drones have a return-to-home function that can assist in this situation.
How do I clean my drone’s propellers?
Gently clean your drone’s propellers with a soft brush and avoid using harsh chemicals. Ensure they are free of dirt and debris before each flight.
What is the best way to store my drone batteries?
Store your drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep them partially charged (around 30-50%) for long-term storage.